- 0120-4438-111
- info@searchmymedical.com
- Office No 519, B Tower, Ithum Tower, Noida Sec 62.
VP Shut
Home > VP Shut
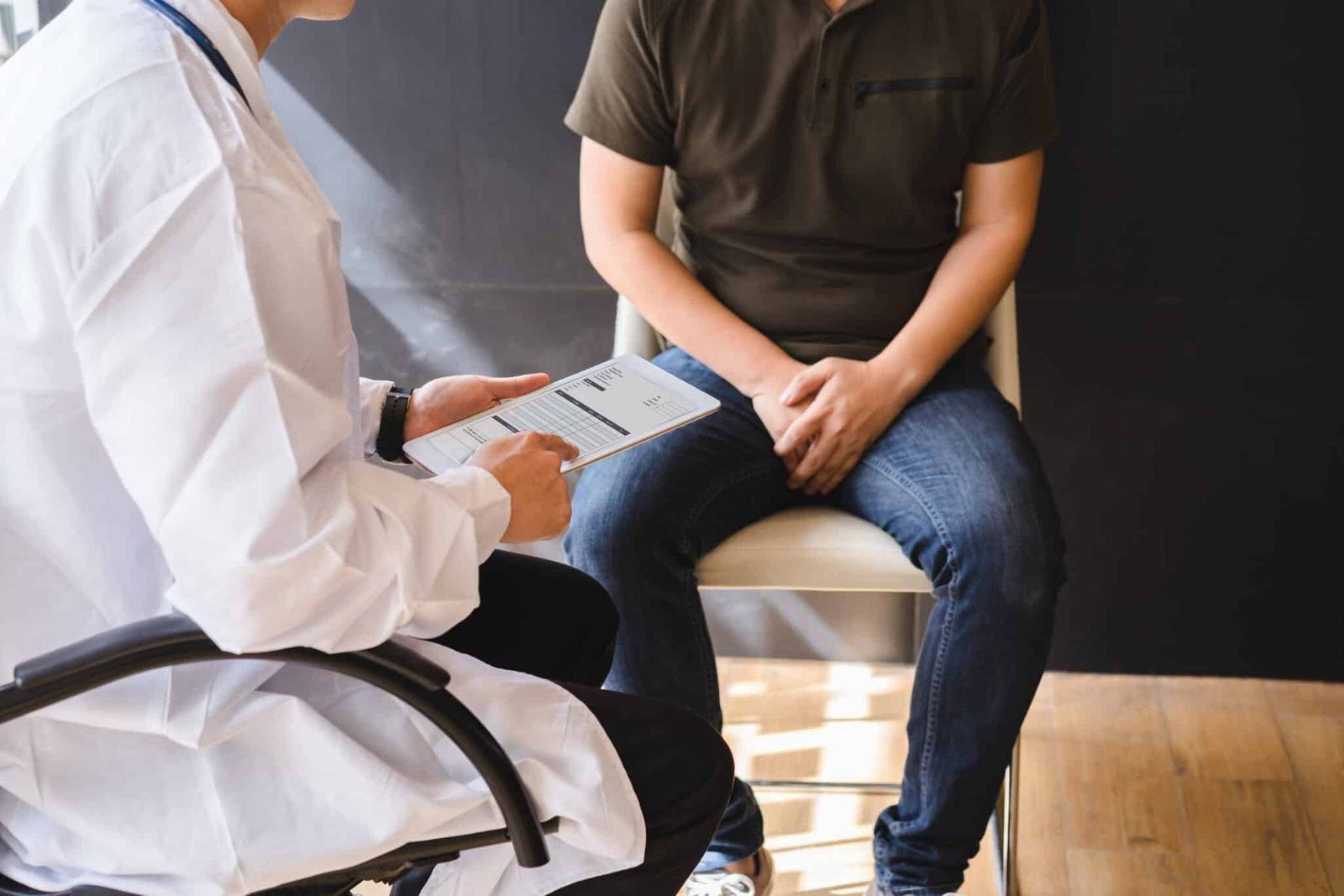

A Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) Shunt is a medical device used to treat hydrocephalus, a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain’s ventricles. This buildup can cause increased intracranial pressure, leading to symptoms like headaches, nausea, vision problems, and cognitive difficulties. The VP shunt helps drain this excess fluid from the brain to another part of the body, usually the peritoneal cavity (the abdominal space), where the fluid can be absorbed naturally.
The procedure to insert a VP shunt involves surgery, typically performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes a small incision in the scalp and drills a tiny hole in the skull to insert the catheter (a thin, flexible tube) into one of the brain’s ventricles. The other end of the catheter is tunneled under the skin and connected to a valve, which regulates the flow of CSF. From there, another catheter is extended from the valve to the peritoneal cavity in the abdomen. This allows the CSF to drain away from the brain, reducing pressure and preventing further complications.
Causes
- Congenital conditions: Some people are born with structural abnormalities that affect CSF flow.
- Acquired conditions: These may include brain tumors, infections (like meningitis), or traumatic brain injuries that block CSF pathways.
Symptoms
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blurred or double vision
- Balance and coordination problems
- Changes in personality or cognitive function
- Enlarged head size in infants
Diagnosis
- Neurological Examination: A thorough assessment of symptoms and neurological function.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans are used to visualize the brain and assess for hydrocephalus or other abnormalities.
Treatment
- Surgery: A neurosurgeon inserts the shunt, which consists of a catheter placed in the brain's ventricles and another catheter leading to the abdominal cavity.
- Post-Operative Care: Monitoring for complications, such as infection or shunt malfunction, is essential.
- Regular Follow-ups: Patients require ongoing monitoring to ensure the shunt is functioning correctly and to manage any potential complications.
How Search My Medical Will Help You
- Access to Accredited Facilities: We connect you with top-tier hospitals
and clinics globally, ensuring high standards of care and patient safety. - Surgeon Selection: Our network includes highly qualified surgeons with
expertise in your specific procedure, ensuring you receive care from the
best professionals. - Appointment Coordination: We handle all logistics related to
scheduling consultations, pre-operative assessments, and surgical
dates, saving you time and effort. - Travel and Accommodation Arrangements: If your procedure is
overseas, we assist with travel logistics, including flight bookings, hotel
accommodations, and local transportation. - Pre-Operative Support: We guide you through necessary preparations,
including medical evaluations and dietary guidelines, to ensure you are
ready for surgery. - Post-Operative Care: After your procedure, we provide resources and
support for recovery, including follow-up appointments and monitoring
your healing process. - 24/7 Assistance: Our dedicated support team is available around the
clock to address any questions or emergencies that may arise during your medical journey.
Latest Post
-
Opps, No posts were found.
Want to consult about health? Contact Us
We ensure a seamless experience. Our network also provides detailed post-surgery support.
Get in Touch
Get in touch with us for any questions or inquiries. We’re here to help and provide the information you need. Reach out via phone, email, or through our website contact form.


Emergency Contact
- Free Call 24/7
- +91 0120-4438-111

Location
- Open In 24 Hours
- SMM, B Tower, Ithum Tower, Noida Sector 62.


Phone Contact
- Within Working Hours
- +91 8810549762
