- 0120-4438-111
- info@searchmymedical.com
- Office No 519, B Tower, Ithum Tower, Noida Sec 62.
Pacemaker Implantation
Home > Pacemaker Implantation
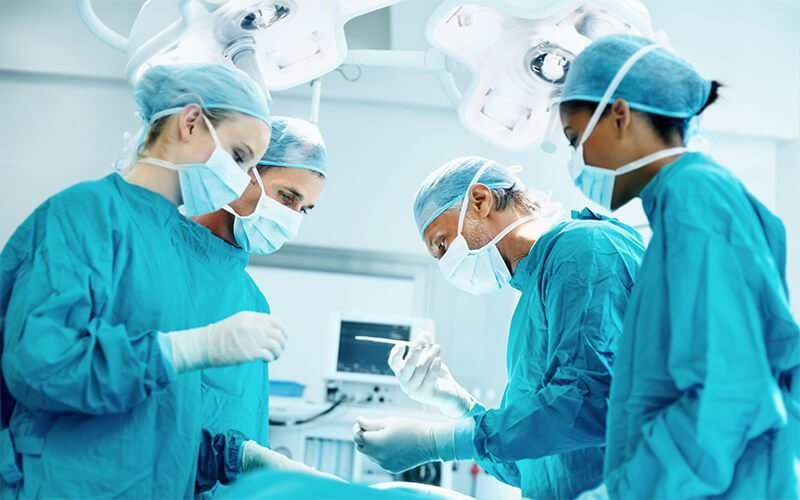

What is Pacemaker Implantation?
Pacemaker Implantation is a surgical procedure to implant a small, battery-operated device under the skin near the heart. The pacemaker sends electrical signals to regulate irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) and ensures your heart beats efficiently.
Pacemaker implantation is a surgical procedure used to treat patients with abnormal heart rhythms, known as arrhythmias, specifically bradycardia (a slow heart rate) or heart block, where the electrical signals that control heartbeats are delayed or blocked. A pacemaker is a small, battery-powered medical device implanted under the skin of the chest or abdomen, designed to help regulate the heartbeat. It does so by sending electrical impulses to the heart muscles to prompt them to contract, thereby ensuring that the heart beats at a normal, healthy rate and rhythm.
The pacemaker consists of two main parts: the pulse generator and the leads (electrodes). The pulse generator houses the battery and the electronics that generate the electrical signals. The leads are thin, flexible wires that are threaded through veins and connected to the heart. Depending on the patient’s condition, the pacemaker may have one, two, or three leads, which are placed in the heart chambers to monitor and stimulate the heart’s activity as needed. The device is programmed by a cardiologist to send electrical signals only when the heart’s natural rhythm falls below a certain threshold.
Why is a Pacemaker Needed?
- Bradycardia: Slow heart rate that causes fatigue or dizziness.
- Heart Block: Delayed electrical signals between heart chambers.
- Tachycardia: Fast, irregular heartbeats that require correction.
- Cardiac Arrest Prevention: Helps in high-risk patients with severe rhythm issues.
- Bradycardia: The most common reason for implantation; it occurs when the heart's natural pacemaker (the sinoatrial node) malfunctions.
- Heart Block: A condition where electrical signals in the heart are partially or completely blocked, causing an irregular heartbeat.
- Sick Sinus Syndrome: A disorder of the heart’s natural pacemaker that leads to irregular heart rhythms.
- Atrial Fibrillation: In some cases, patients with atrial fibrillation may require a pacemaker if they also experience bradycardia.
The Pacemaker Implantation Procedure
-
Preparation:
- Performed under local anesthesia and mild sedation.
- Patient’s chest area is sterilized, and an incision is made below the collarbone.
-
Device Placement:
- Wires (leads) are inserted into a vein and guided to the heart chambers.
- Leads are connected to the pacemaker, which is implanted under the skin.
-
Testing and Closure:
- The pacemaker is tested to ensure proper function.
- The incision is closed with sutures.
- Single-Chamber Pacemaker: This type has one lead that connects to either the right atrium or right ventricle, pacing one chamber of the heart.
- Dual-Chamber Pacemaker: This type has two leads, one in the right atrium and one in the right ventricle, allowing for more coordinated pacing of both chambers.
- Biventricular Pacemaker: Used for cardiac resynchronization therapy, it has three leads and is designed to coordinate contractions between the left and right ventricles in patients with heart failure.
Benefits of Pacemaker Implantation
- Restores normal heart rhythm and improves blood circulation.
- Reduces symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, and fainting.
- Enhances quality of life and physical activity levels.
- Decreases risk of severe complications like stroke or cardiac arrest.
Post-Implantation Recovery
-
Immediate Recovery:
- Hospital stay of 1-2 days for monitoring.
- Mild pain or bruising at the implant site is common.
-
Long-Term Care:
- Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for 4-6 weeks.
- Regular check-ups to monitor device function and battery life.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Avoid close proximity to strong electromagnetic fields (e.g., MRIs or industrial equipment).
- Notify medical staff of your pacemaker before undergoing procedures.
Risks and Complications
While rare, potential risks include:
- Infection at the implant site.
- Bleeding or bruising from the procedure.
- Device malfunction, requiring reprogramming or replacement.
- Lead dislodgement, needing repositioning.
How Search My Medical Will Help You
- Find Specialists: Easily locate top cardiologists and cardiac surgeons specializing in Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) and other heart related procedures.
- Comprehensive Information: Access detailed resources about CABG, including what to expect during the procedure, recovery tips, and potential risks, empowering you to make informed decisions.
- Patient Reviews: Read testimonials from other patients who have undergone CABG, helping you choose the right healthcare provider based on real experiences.
- Appointment Booking: Streamline the process of scheduling consultations and follow-up appointments directly through our platform, saving you time and effort.
- Second Opinions: Facilitate consultations with multiple specialists to ensure you receive the best possible care and validate your treatment options.
Latest Post
-
Opps, No posts were found.
Want to consult about health? Contact Us
We ensure a seamless experience. Our network also provides detailed post-surgery support.
Get in Touch
Get in touch with us for any questions or inquiries. We’re here to help and provide the information you need. Reach out via phone, email, or through our website contact form.


Emergency Contact
- Free Call 24/7
- +91 0120-4438-111

Location
- Open In 24 Hours
- SMM, B Tower, Ithum Tower, Noida Sector 62.


Phone Contact
- Within Working Hours
- +91 8810549762
