- 0120-4438-111
- info@searchmymedical.com
- Office No 519, B Tower, Ithum Tower, Noida Sec 62.
MBG (Bariatric)
Home > MBG (Bariatric)
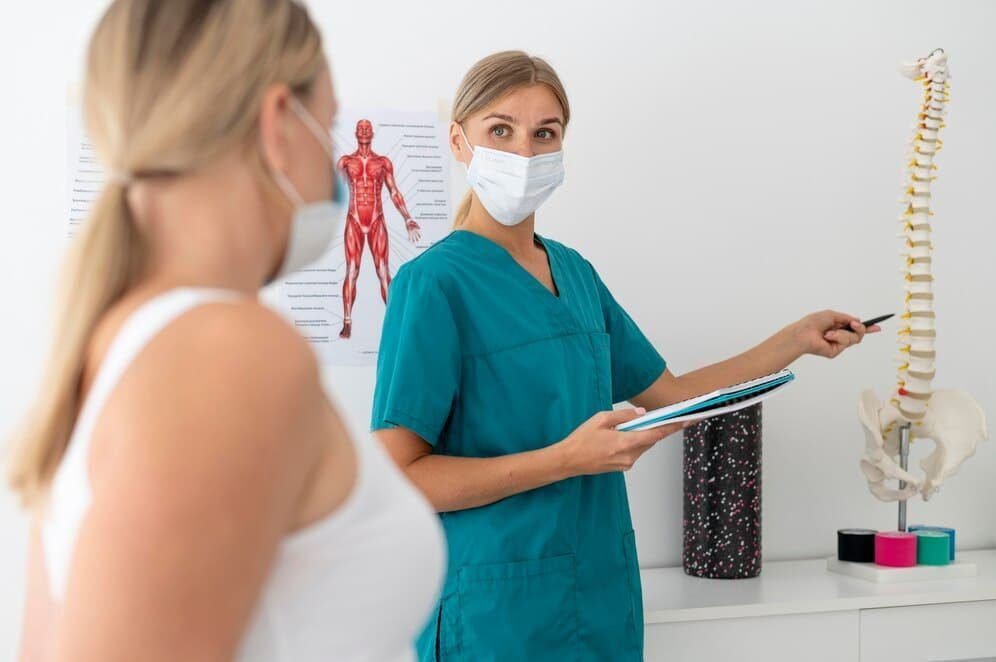

What is MBG (Bariatric Surgery)?
MBG (Bariatric Surgery) refers to a group of surgical procedures designed to help individuals struggling with obesity lose weight. These surgeries alter the digestive system to limit the amount of food a person can eat or reduce nutrient absorption. MBG surgery is often recommended for individuals who are severely obese and have not been able to lose weight through diet, exercise, or other weight-loss methods.
Types of MBG Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery encompasses several different types of procedures, each designed to aid in weight loss. The most common types include:
-
Gastric Bypass Surgery (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass):
Gastric bypass surgery involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach and rerouting the small intestine to this pouch. This limits the amount of food a person can consume and reduces nutrient absorption, promoting weight loss. -
Sleeve Gastrectomy (Gastric Sleeve):
In this procedure, approximately 80% of the stomach is removed, leaving a tube-shaped stomach (the sleeve). This smaller stomach reduces food intake, leading to significant weight loss. -
Adjustable Gastric Banding (Lap-Band Surgery):
In gastric banding surgery, a band is placed around the upper portion of the stomach to create a small pouch. The band can be adjusted to control food intake. This procedure is less invasive than gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy. -
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS):
This complex surgery involves removing a portion of the stomach and rerouting the intestines to limit both food intake and nutrient absorption. It leads to substantial weight loss but carries a higher risk of nutritional deficiencies. -
Endoscopic Bariatric Procedures:
These non-surgical procedures involve using a scope to perform treatments like gastric balloon placement, which reduces stomach capacity and helps with weight loss.
Who Should Consider MBG Bariatric Surgery?
MBG Bariatric Surgery is typically recommended for individuals who:
- Have a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher (severe obesity).
- Have a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea.
- Have unsuccessfully tried other weight-loss methods (dieting, exercise, medications).
- Are committed to making long-term lifestyle changes post-surgery.
The MBG Bariatric Surgery Procedure
The MBG Bariatric Surgery procedure typically involves the following steps:
-
Pre-Surgery Consultation and Assessment:
Before undergoing surgery, patients must have a thorough evaluation, including physical examinations, psychological assessments, and nutritional counseling. -
Anesthesia:
Bariatric surgery is generally performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient is asleep during the procedure. -
Surgical Procedure:
Depending on the chosen procedure (e.g., gastric bypass, gastric sleeve), the surgeon will either create a smaller stomach pouch or place a band around the stomach to limit food intake. Some procedures, like gastric bypass, involve rerouting the intestines. -
Post-Operative Care:
After surgery, patients are monitored in the hospital for a few days. The medical team will ensure proper healing and manage any immediate post-operative concerns.
Recovery After MBG Bariatric Surgery
Recovery after MBG Bariatric Surgery varies depending on the type of procedure performed. However, the general recovery process includes:
-
Hospital Stay:
Most patients stay in the hospital for 2-3 days after the surgery to monitor recovery and address any complications. -
Dietary Changes:
Immediately after surgery, patients are required to follow a liquid diet and slowly transition to solid foods over several weeks. Eating smaller, frequent meals is essential. -
Physical Activity:
Exercise is a vital component of the recovery process. Patients are encouraged to start light physical activity soon after surgery to aid weight loss and improve overall health. -
Long-Term Lifestyle Changes:
Patients must commit to a healthy, balanced diet and regular physical activity long-term. The success of bariatric surgery heavily depends on the patient’s ability to adapt to these lifestyle changes.
Benefits of MBG Bariatric Surgery
-
Significant Weight Loss:
Bariatric surgery can help individuals lose a substantial amount of weight, leading to improved overall health. -
Improved Quality of Life:
Many patients experience enhanced mobility, energy levels, and self-esteem after significant weight loss. -
Improved Health Conditions:
Bariatric surgery can help improve or resolve obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and joint pain. -
Reduced Risk of Serious Diseases:
Bariatric surgery reduces the risk of developing certain cancers, heart disease, and other obesity-related diseases.
Risks and Complications of MBG Bariatric Surgery
While bariatric surgery is generally safe, there are some risks and potential complications, including:
-
Infection:
As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the surgical site. -
Nutritional Deficiencies:
Because some procedures limit nutrient absorption, patients may need to take lifelong vitamin and mineral supplements to prevent deficiencies. -
Blood Clots:
Blood clots can form after surgery, especially if the patient is not mobile for an extended period. -
Gallstones:
Rapid weight loss after bariatric surgery can increase the risk of developing gallstones. -
Dumping Syndrome (for Gastric Bypass):
This occurs when food moves too quickly through the stomach and small intestine, causing nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Post-Operative Care and Follow-Up
-
Regular Check-ups:
Patients need regular follow-up appointments to monitor weight loss, ensure proper healing, and address any nutritional deficiencies or complications. -
Lifestyle and Dietary Counseling:
Continued counseling and support are crucial to maintaining the weight loss results and overall health post-surgery.
How Search My Medical Will Help You
- Specialized Search: You can search for surgeons who specialize in the
specific type of surgery you need, ensuring that you’re in the hands of an expert. - Patient Reviews and Ratings: Read reviews from other patients to get
insights into the surgeon’s experience, bedside manner, and overall patient
satisfaction. - Flexible Options: You can often choose from a variety of appointment times
and dates to accommodate your schedule. - Treatment Options: Learn about different surgical options available for your
condition, along with the associated risks, benefits, and recovery times. - Appointment Coordination: We manage all aspects of scheduling your
surgery, including initial consultations, pre-operative assessments, and the
surgical date. - 24/7 Assistance: Our team is available around the clock to address any
concerns or emergencies that may arise during your journey.
Latest Post
-
Opps, No posts were found.
Want to consult about health? Contact Us
We ensure a seamless experience. Our network also provides detailed post-surgery support.
Get in Touch
Get in touch with us for any questions or inquiries. We’re here to help and provide the information you need. Reach out via phone, email, or through our website contact form.


Emergency Contact
- Free Call 24/7
- +91 0120-4438-111

Location
- Open In 24 Hours
- SMM, B Tower, Ithum Tower, Noida Sector 62.


Phone Contact
- Within Working Hours
- +91 8810549762
